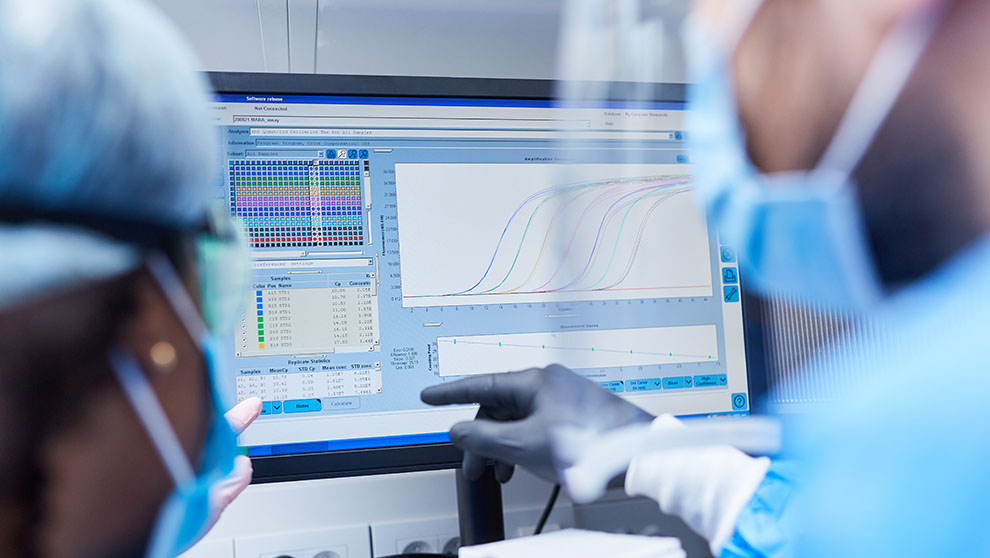
For researchers, clinical data management and reporting has historically included manual curation and compilation of datasets from disparate data warehouses. In today’s data-rich environment, manual processing and integration is becoming more and more of a bottleneck.
In order to keep up with the increasing amount of data collected from clinical research, clinicians and statisticians alike need software tools that will centralize their data and help them quickly recognize errors. LabKey Server provides essential tools to overcome these, and other key clinical research challenges including:

Maintaining Clinical Data Integrity
Having an accurate representation of clinical data helps transform discoveries and understanding into patient care and treatment. Centrally-housing data in a compliant environment that enforces data standardization can help clinicians maintain excellent data integrity and provide an authoritative view of their data landscape.
LabKey Server helps maintain data integrity by providing:
- A highly structured data environment with enforceable data fields to ensure data is entered correctly and within range
- Quality control measures such as data flags, QC of datasets and built-in QC reports
- Role and group-based permission levels that allow users only access to what they need access to
- A compliance module, the allows users to set PHI securities, set Terms of Use for users, and provide electronic signatures on data snapshots
 Integration of Data from Multiple Sources
Integration of Data from Multiple Sources
Bringing together data from disparate sources into a single system can help clinical research stay on track and on time. Collaborative monitoring of data quality by clinicians, statisticians, and scientists enables quick identification of erroneous data and ensures a reliable, integrated data landscape for comprehensive data analysis.
LabKey Server helps facilitate comprehensive data integration by providing:
- Management of lab data together with clinical data in a single system
- A study module that can recognize and integrate disparate vendor datasets
- Built-in and customizable integration with electronic data capture systems and case report forms
- A clinical document abstraction pipeline, which can extract valuable data from legacy documents
 Secure Reporting and Collaboration
Secure Reporting and Collaboration
A key component of effective clinical data management is the ability to share reports and data with collaborators to improve research, innovation, and ultimately patient care. Maintaining compliance and having the ability to quickly share data and reports is an important topic to tackle in clinical research where patient safety and care is the top priority.
LabKey Server improves reporting and collaboration by providing:
- Dynamic and static reporting tables and visualizations that can be shared as-needed
- Web-based access to a central platform for data sharing
- The ability to remove PHI fields or provide randomized IDs when sharing information with collaborators
With the right tools for clinical data management, research teams can eliminate data integration bottle necks and curate reliable datasets for analysis. Explore our example Longitudinal Study or Sign-up for a free trial to see how LabKey Server can help your team overcome these, and other common clinical research challenges.
Related Documentation
Read more about the features highlighted above on the LabKey Support Portal: